The Details
So you’re ready to start composting. It’s a fantastic way to reduce waste, help the planet, and create rich, fertile soil that’s excellent for gardening. There are several ways to compost, ranging from composting using an industrial compost facility to composting right in your backyard. If you’re trying to find the best way to compost, keep reading!
WHAT IS COMPOSTING
Composting is the process of taking organic material and using human activity to help it break down more readily. Compostable materials like food scraps, paper waste, produce, and yard clippings can all break down into soil that is excellent for fertilizing gardens. Tossing these items in a compost rather than a landfill allows them to break down more quickly with greater aeration, and produces less methane gas that contributes to global warming. In short, it’s an easy way to help the planet!
There are several grades of compostability with various certifications, namely home compostable and commercially (also known as industrially) compostable. Here are the main differences between home and industrial composting.
Home Composting
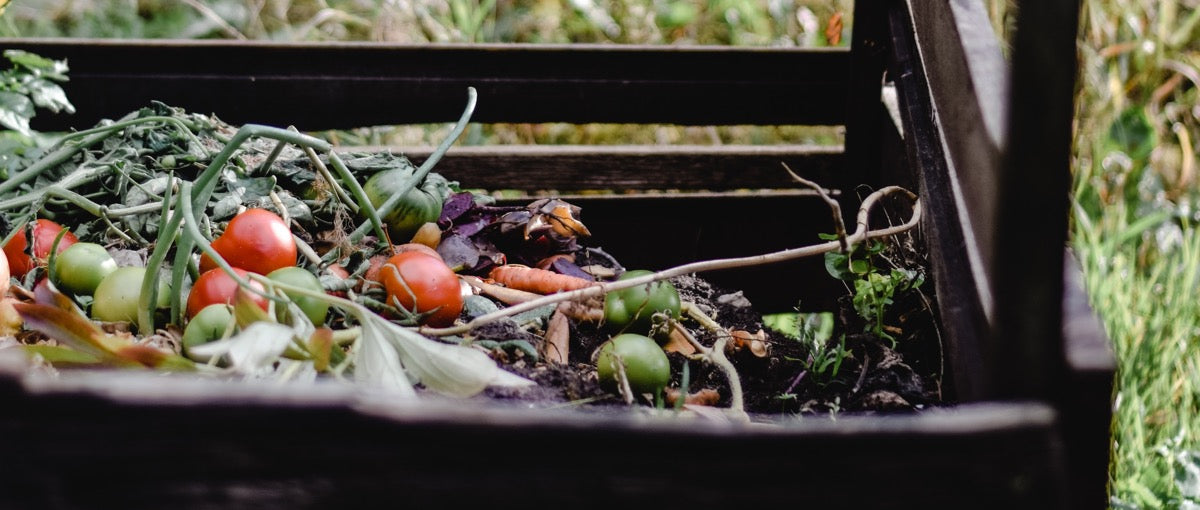
Home compostable goods break down under normal home compost conditions. This means lower heat and moisture levels than industrial composting, which is heavily regulated to compost more efficiently. Organic matter like fruits, veggies, dried eggshells, and lawn trimmings are home compostable. If you want to find out if a manufactured item is home compostable, look for the TUV Certified Home Compostable seal.
How to Compost At Home
Composting at home is easy and efficient. To get started, follow these steps:
1. FIND YOUR STORAGE BIN. Use a small metal or ceramic bin with a lid to keep in odors. Line with a HoldOn compostable compost bag and store where you'll need it most - the kitchen is an ideal spot to collect food scrap waste.
2. CREATE A DEDICATED COMPOST SPACE. Use a compost barrel or bin, or even begin a compost pile on bare soil. A shady spot is ideal for composting, as it will help your compost to maintain proper moisture levels.
3. LAY A FOUNDATION. Prep your outdoor compost with twigs and straw, which will help to aerate your pile and keep it from becoming too dense.
4. IDENTIFY what to compost. As a general rule of thumb, materials that come from the earth are compostable. Do not compost inorganic materials, as they won't break down, as well as meat or dairy, which may attract pests.
5. TURN OVER occasionally. This will aerate materials and help them to decompose evenly.
Learn more by visiting our quick-start composting guide.

Commercial Composting
Most compost services, like pick up or drop off services, utilize an industrial compost system. Industrial (also known as commercial) composting uses higher heat and moisture levels to speed up the decomposition process, which lasts just a few days or weeks. In addition, most products labeled ‘compostable’ are industrial compostable. You can use a municipal or pick-up service to compost these goods, but they will not break down in your home compost. All items that are home-compostable are also commercially compostable. If you’re unsure if an item can be commercially composted, look for the BPI Commercially Compostable Certification.